Roses can be propagated in various ways - seed, layering, grafting and cuttings. Many lovers prefer to propagate roses by cuttings. This method is not as fast as propagation by vaccination, but with it a longer-lived plant grows, and there is no need to fight the shoot. Consider the different methods of grafting roses, and which varieties are best to choose for this, how to transplant rooted cuttings to a permanent place and care for them.
What varieties of roses can be propagated by cuttings?
Cuttings are not used for all varieties of roses. Miniature, polyanthus and hybrid-polyanthus varieties, groundcover and climbing roses with small flowers are perfectly rooted. Cuttings of floribunda roses are rooted at 50%. Hybrid tea, park, climbing roses with large flowers do not tolerate this method well, and give roots reluctantly, but amateur gardeners sometimes succeed even when they are rooted. Among scrubs, rooting of cuttings of roses of English selection (Austin) gives a good result.
For rooting, it is best to choose these varieties of roses:
- miniature - Border King, Lupo;

- polyanthus - Border King, Paul Crampel, Holsiein;

- ground cover - Bonica, Drift, Larissa Anadia;

- English - William Morris, Abraham Darby;

- wicker with small flowers - Bobbie James, Snow goose, Polka;

- floribunda - Apricola, Edelweiss, Tequila.

It is believed that for cuttings it is best to choose roses of red or pink color. White varieties are slightly behind them. The worst-rooted yellow tea hybrid roses. However, this rule does not always apply. Florists note that many old well-deserved varieties take root well. For example, tea-hybrid rose Gloria Day with a luxurious golden pink color, which is the standard for all roses.
Cuttings are an affordable material for propagation. They can be cut even from a bouquet. However, it will be more reliable if the bouquet is seasonal and from local roses. Roses imported to us from the Netherlands are usually processed with chemicals and are often overexposed in the cold. Each class has its own greenhouse, and it’s not a fact that a rooted plant can grow in your garden in the open ground. Although experimentation lovers may try to do this.Did you know? The Gloria Day rose variety was bred in the 30s of the last century by the Frenchman Francis Mayian. A small number of cuttings were sent to several countries, but World War II did not immediately allow this variety to be registered. Now it exists under four names - Madame Meyan (France), Delight (Italy), Gloria Day (Germany), World (USA). In the post-Soviet space, the German name has taken root.
Cutting time
The best time for grafting roses is the period from the beginning of spring to mid-summer. This gap allows the cuttings to take root well and postpone the subsequent wintering. In the southern regions, it is possible to successfully cuttings in August, since warm autumn usually gives time for cuttings to take root and prepare for the cold season.
Preparation for breeding
Cuttings are most reliable to take from adult plants. To do this, choose the strongest semi-woody shoot of the current year, and cut from its middle part cuttings of about 10–20 cm with 2-3 buds each. It is best to take shoots in the lower or middle part of the rose bush.
The lower parts of the cuttings are cut immediately under the kidney obliquely at an angle of 45 °, so that the plant can take root. The upper cut is made even 5 mm above the upper kidney. The lower leaves are removed from the cuttings, and the two upper pairs are shortened by a third.Important! The selected shoot should not be too thin (less than 3-4 mm) or too thick (thicker than 8 mm). It must be healthy, without signs of disease or pest damage.
Possible picking cuttings in the fall. In this case, thick woody annual shoots are gaining, which often remain after the autumn pruning of rose bushes. They are removed leaves and stored until spring in a moist mixture of sand and peat at 0 ° C. Such cuttings in spring lend themselves well to rooting. If you want to cut roses from a bouquet, then it should be as fresh as possible, and cuttings from it should be cut as quickly as possible. For cuttings, specimens are taken without the slightest sign of withering and with a sufficient thickness of the stem, in the middle of which there must be at least two buds. Slices are made in the same way as when taking cuttings from the bush.
If you want to cut roses from a bouquet, then it should be as fresh as possible, and cuttings from it should be cut as quickly as possible. For cuttings, specimens are taken without the slightest sign of withering and with a sufficient thickness of the stem, in the middle of which there must be at least two buds. Slices are made in the same way as when taking cuttings from the bush.
Rooting methods
You can root a rose stalk at home using different methods. Most often, plants are germinated in water or in containers with soil. But there are other, more unusual, but no less effective ways. This is sprouting with the help of bags, newspapers and potato tubers.
But no matter what method you choose, it should be borne in mind that the optimal conditions for growing rose cuttings are a warm room (+ 22 ... + 25 ° C), high humidity (90–100%) and good, but diffuse lighting. Such plantings should be protected from direct sunlight.
In water
Perhaps the easiest method is the germination of the cuttings in water. Rain, spring water or from a well is well suited for this process.
The acceleration process itself occurs in this way:Important! If tap water is used for rooting, then it must be filtered and allowed to settle for at least a day.
- Pour some water into a glass jar.
- Prepared seedlings are placed in water at 1.5-3 cm. Too much immersion in water is not worth it, as this can lead to decay.
- The jar is put in any place where there are no direct rays of the sun.
- Water is replaced every two days.
- After about 20-22 days, the root system is formed. First, white growths appear on the plant from below, and then roots grow from them.

In pots
This method is great when you need to root a stalk at home, for example, from a bouquet.
To do this, perform the following steps:
- The cut stalk is treated with root stimulators of the Kornevin type.
- The treated process is placed in the prepared soil, for example, from a mixture of equal parts of humus and turf. Shortly before planting, this soil mixture should be decontaminated with a solution of potassium permanganate or by calcination in the oven. Or you can just buy ready-made universal primer in the store.
- The stem is buried in the prepared soil, covered in a half-liter pot, by several centimeters.
- Top planting is covered with a jar to create the optimal microclimate for the appearance of roots.

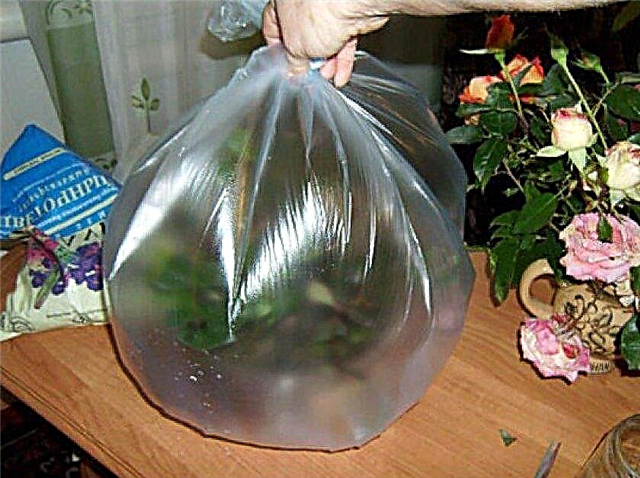
In the package
The use of rooting bags allows for optimal moisture and a greenhouse effect for the plant. For this simple method, you do not need to purchase containers for landing.
This rooting method is done this way:
- The package is filled to a third with prepared soil.
- Treated with growth stimulant cuttings are placed in the soil.
- The rest of the space in the bag is filled with air and suspended such a structure near the window.

In the newspaper
The process of rooting seedlings in a newspaper is also called the “burritto method”. Externally, cuttings wrapped in a newspaper are really similar to this product.
To do this, you need to prepare the following materials:
- plastic bags;
- Newspapers
- cut cuttings.
Did you know? An unusual rose variety has been partitioned in Japan. In the morning the flower petals are red, and in the evening they become white. This variety was given the name "Chameleon".
The acceleration process itself occurs in this way:
- Several cuttings are laid out on a newspaper sheet.
- The newspaper is bent above and below, and then seedlings are wrapped. It looks like a small roll, inside which plants are placed.
- The resulting roll is moistened with water, but so that the paper does not spill.
- Then this bundle is placed in a bag made of polyethylene and knotted.
- Once every 7 days, you need to open the plastic bag, unfold the paper and inspect the cuttings, and then moisten them. In the case when some cuttings began to rot, they are removed, and the newspaper is replaced with a new one.
Video: rooting roses in a newspaper
Using potatoes
If the rooting of the cuttings occurs with the help of potatoes, then the necessary humidity of this vegetable and the replenishment of healthy carbohydrates are a positive factor. This method gives strong young seedlings, on the root of which little effort has been expended.
First you should choose potato tubers. They should be medium in size with no signs of rot, disease, or any damage. Selected specimens are washed and placed in a solution of manganese for disinfection. Then the potatoes are dried, and it is completely ready for further use.
The rooting process itself is carried out as follows:
- A groove is cut out in the potato, which almost reaches the other side of the vegetable. The width of the hole should correspond to the thickness of the handle.
- A section of the seedlings is treated with a growth stimulator and placed in a tuber hole.
- Pour some earth into a container or pot and place a tuber on it. The soil is poured on top, slightly tamping it. Be sure to water it.
- To create a greenhouse effect, everything is covered with a glass bottle on top.
Video: rooting roses in potatoes
Open transplant
It is recommended to plant rooted seedlings of roses in the ground in the spring in May or early summer, when there are no more frosts and the ground has warmed enough. The landing area should be in the sun and also protected from the wind. It should be flat, not in a pit or ravine, so that there is no stagnation of water in rainy times.
The soil for planting is preferable to choose fertile and light. Heavy soil can be made suitable for planting roses by applying a mixture of coarse sand, peat and humus at the rate of 1 bucket of mixture per 1 m².
Due to the fact that the roots go deep into the soil, the groundwater level should not come closer than 1 m to the surface of the earth. Otherwise, the root system of roses will rot, which will lead to the death of the plant.
Dig the soil before planting, and also make organic and complex fertilizers for flowering crops. Landing holes are dug up to the size of the root system. Organic fertilizers (rotted manure) are placed in each such pit. The seedling is carefully placed in a hole, spreading the roots, and sprinkled with earth. After each bush is mulched with peat, sawdust from a tree. From direct sunlight, the landing is protected by covering material.Important! The distance between the seedlings is maintained depending on the variety of roses. Curly roses plant with an interval of 1.3–2 m from each other. Ground-cover roses, which grow well, are planted at intervals of 0.5–0.8 m, and species of small sizes are 0.3–0.4 m.
Active growth of seedlings occurs after 10-14 days, when the root system is fully adapted on the site.

Features of care for seedlings
Further care for rose seedlings consists of watering, fertilizing, protecting against diseases and insect pests, as well as shelter in the cold.
As soon as the seedlings reach 12-14 cm, they are fed with complex fertilizers, herbal infusions or rotted mullein. In the future, fertilizers should be applied from spring to the second half of summer, and especially during the formation and growth of buds. Toward the end of summer, dressing is stopped so as not to cause active shoot growth.
In the first year, when the rose bushes take root in a new place, you need to remove all the buds that have appeared so that the flower does not waste its energy on flowering, but throws them to form good stems.
The roots of these beautiful flowers go deep into the ground. Therefore, to prevent water from spreading, a small moat is made around each bush. Watering is carried out abundantly - 10-12 liters for each plant. During the period of active growth, when buds are formed, watering should be monitored especially carefully. Roses are constantly loosening 5-10 cm in depth. At the same time, weed removal is performed. It is also useful to mulch peat, humus.Did you know? Roses were grown in ancient Rome, and even then they were not of the same variety. Herodotus still mentions this beautiful flower in the 5th century. BC e. In his History, he writes about a terry rose in the gardens of King Midos in Macedonia.
In autumn, it is imperative to provide young flowers with shelter from frost. In preparation for wintering, buds and leaves are cut, and also sprayed with copper sulfate to reduce the risk of fungal and bacterial diseases.
Places of cuts are treated with garden var. Only then they cover the bush with peat, soil from another site, humus, or sawdust to a height of 25–30 cm. For the winter, the climbing and stem species of roses are not cut, but bent to the ground, pulling the shoots with ropes, and then covered with spruce branches or covering material (roofing material )
In the spring, the shelter is removed and treated with a solution of copper sulfate. Weak and damaged shoots prune.
Some valuable types of bushes should be dug up and moved for storage in the winter to a cool, damp room. Humidity should be constantly maintained so that the roots do not dry out.
Root cuttings are easy to root, but you should take into account some of the nuances. There are different ways to root them, and you can choose the most suitable for you.